Technical visits
Congress members were able to take part in a number of technical visits arranged to showcase Andorra's technical infrastructure and facilities for managing winter road conditions, which also enabled congress members a novel experience.
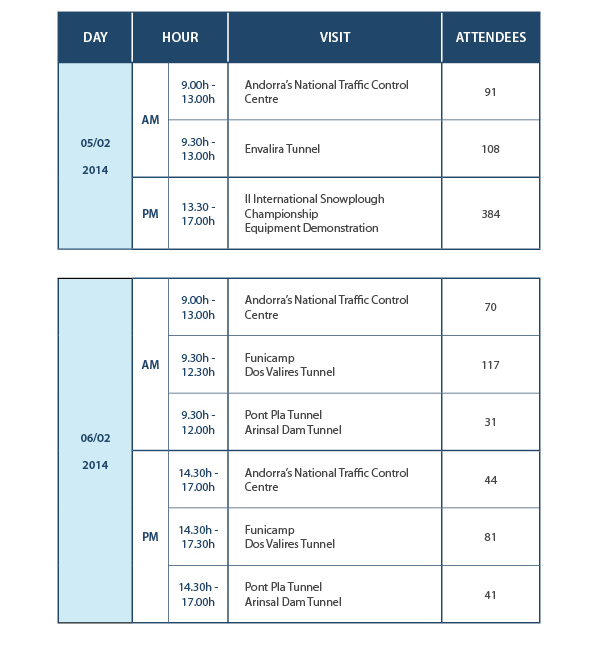
The technical visits were held over two days during the week of the Congress: Wednesday 5 and Thursday 6 of February.
The full programme and overall attendance at the technical visits were as follows:
A brief description of each visit is provided hereon.
| Andorra's National Traffic Centre |
 The National Traffic Centre is the principal area which controls Andorra's road network. Its main function is to keep road users informed about traffic and road conditions. This is done through use of variable telematics and information systems, emergency services information and coordination, and management of reversible lanes used by public transport and traffic lights. All such measures are taken 365 days a year, 24 hours a day. The National Traffic Centre is also in charge of tunnel surveillance via the Andorran Tunnel Control Centre. To carry out this task, a Multi-Tunnel computer program is used, which provides information about any incident with tunnel security, control and/or communication devices. It also coordinates preventative and correctional maintenance tasks.
The National Traffic Centre is the principal area which controls Andorra's road network. Its main function is to keep road users informed about traffic and road conditions. This is done through use of variable telematics and information systems, emergency services information and coordination, and management of reversible lanes used by public transport and traffic lights. All such measures are taken 365 days a year, 24 hours a day. The National Traffic Centre is also in charge of tunnel surveillance via the Andorran Tunnel Control Centre. To carry out this task, a Multi-Tunnel computer program is used, which provides information about any incident with tunnel security, control and/or communication devices. It also coordinates preventative and correctional maintenance tasks.
The visit to the National Traffic Centre will give visitors the opportunity to see how two areas are operated: the Centre of Information and Traffic Management and the Tunnel Control Centre. Visitors will learn about the different systems used to inform road users about road conditions and potential incidents, as well as how the Multi-Tunnel system detects incidents. Those who go on this visit will also discover what steps are taken when accidents occur inside tunnels and how vehicles transporting hazardous goods are detected. In terms of winter road safety, the snow removal machine control system will be shown in real-time, along with information about the vehicles offered by the system. Visitors will also be able to see how the Express Bus line between the parishes of Escaldes-Engordany and Sant Juli� de L�ria operates. |
| Envalira Tunnel |
 The Envalira Tunnel belongs to GLOBALVIA INFRAESTRUCTURAS, an international group and world leader in transportation infrastructure management.
The Envalira Tunnel belongs to GLOBALVIA INFRAESTRUCTURAS, an international group and world leader in transportation infrastructure management.
Prior to the tunnel's construction, the Envalira port was the only route connecting Andorra and France. This road, however, has slopes with steepness greater than 8% and an altitude reaching 2.408 meters. This, in turn, often leads to traffic problems during the winter due to weather conditions. Along with its construction and within an administrative concession regime, the Andorran government formed a new route connecting Andorra and southern France directly and safely. This route has also been integrated into the overall trans-Pyrenean communication network. Technical visits have been planned to the Globalvia Envalira Tunnel during the XIVth International Winter Road Congress. This tunnel is distinguished from the rest of European tunnels due to its particularities and altitude which reaches up to 2050m, the highest of such classification. |
| Funicamp |
 Funicamp is the only funitel gondola lift found among the Pyrenees. It's found at Grandvalira's ski resort and links the ski stations of Pas de la Casa, Grau Roig, Soldeu, el Tarter and Canillo together. Thanks to Funicamp, two areas have been connected, Grandvalira's ski station with Encamp's center.
Funicamp is the only funitel gondola lift found among the Pyrenees. It's found at Grandvalira's ski resort and links the ski stations of Pas de la Casa, Grau Roig, Soldeu, el Tarter and Canillo together. Thanks to Funicamp, two areas have been connected, Grandvalira's ski station with Encamp's center.
The funitel system is a means of high capacity cable transport. The passenger cabins are connected to a pair of cables and are able to tolerate high wind speed. Funicap was built in 1998 by Doppelmayr. A smaller station can be found at its center which houses 2 motor groups. The line has a total length of 5,6 km and travels at a speed of 7,2 m/s, making it the fastest gondola lift in the Pyrenees. The structure is made up of two different cables, one on the upper part and another on the lower one. The line has an initial sharp rise which then evens out and continues uniformly. The remaining 400m of the second part of the gondola lift, has a gradual slope gradient. The cabin has a 24-person capacity, is sustained by 4 grips and is able to transport 3,400 people per hour. |
| Dos Valires Tunnel |
 In its first phase of operation, the New Road Infrastructures Sector Plan contemplated the Dos Valires Tunnel. This is a double unidirectional tunnel with a two-lane road at each driving direction. It connects two the of the three main Andorran valleys: The Northern Valira River and the Eastern Valira River, which are areas found at the bottom of La Massana and Encamp.
In its first phase of operation, the New Road Infrastructures Sector Plan contemplated the Dos Valires Tunnel. This is a double unidirectional tunnel with a two-lane road at each driving direction. It connects two the of the three main Andorran valleys: The Northern Valira River and the Eastern Valira River, which are areas found at the bottom of La Massana and Encamp.
This tunnel was built in 4 phases: excavation, lining, construction of both entrances and facilities. The construction started in 2005 and was completed in 2011 and the total investment was of 157 million euros. The tunnel is nearly 3km long and is equipped with a central evacuation gallery and services. The central gallery and both the tunnel sections are interconnected by 8 pedestrian galleries and 3 other ones suitable for emergency vehicles. The total length between the evacuation galleries is of around 260 meters and network services run through the central gallery and connect both the tunnel sections. The whole tunnel is lined and the sidewalls are painted to optimize their illumination and to give it a nice final touch. The tunnels' current speed limit is 80km/hr, with a turning radius around 2000 meters and an anti-symmetric track. One of the peculiarities this tunnel offers is that it permits trucks of over 3.5 tons to go through it, including those transporting dangerous goods. This means that the tunnel had to be specially equipped keeping this in mind. It currently disposes of the following featrues: DAI, lighting, a sound system, a VASCAR radar, cross-arrows, traffic lights, and ADR plate readers at the tunnels' mouths, among others. All these elements have been centralized at the Local Control Center (CECOL) and the National Traffic Centre (CENATRA) located in the administrative building of Prado Rull (Andorra la Vella). In addition, the National Traffic Center established a special protocol for trucks passing through the tunnel transporting dangerous goods. |
| Pont Pla Tunnel |
 The Pont Pla Tunnel is a two-way tunnel with a total length of 1,291 meters, along with 1,275 meters of evacuation galleries and parallel services, connected among one another by 7 connecting galleries, each one 160 meters in size. All galleries are suitable for pedestrian evacuation and the central one is also fit for the passage of emergency vehicles. The construction of the Pont Pla Tunnel was a major challenge in terms of safety conditions during the excavation and maintenance. This was due to its singular characteristics as it is found in the city center and has a longitudinal gradient of 7%. This tunnel was built following the so-called 'New Austrian Method', which is based on the use of a tunnel vault to diminish the state of the tensions generated by the thrust of the rock mass, in order to stabilize the tunnel.
The Pont Pla Tunnel is a two-way tunnel with a total length of 1,291 meters, along with 1,275 meters of evacuation galleries and parallel services, connected among one another by 7 connecting galleries, each one 160 meters in size. All galleries are suitable for pedestrian evacuation and the central one is also fit for the passage of emergency vehicles. The construction of the Pont Pla Tunnel was a major challenge in terms of safety conditions during the excavation and maintenance. This was due to its singular characteristics as it is found in the city center and has a longitudinal gradient of 7%. This tunnel was built following the so-called 'New Austrian Method', which is based on the use of a tunnel vault to diminish the state of the tensions generated by the thrust of the rock mass, in order to stabilize the tunnel.
The infrastructure installation phase was a very important one from the point of view of planning the necessary security as well as tunnel management and control. This was due to the tunnel's slope gradient and the fact that traffic of around 23,000 vehicles per day, concentrated during peak hours, was expected. The tunnel was built according to the most stringent regulations available at the time of its construction and it has, among others, an autonomous power system supply, variable traffic signals, automatic incident detection, a fire detector, anti-fire and sanitary ventilation, SOS signs, fire hydrants, and evacuation gallery pressurization. All the above is managed and controlled by a local control center (CENATRA). The Pont Pla Tunnel received merit in 2008 when it was rated Europe's best tunnel by the EuroTAP program, which is endorsed by 14 European organizations as well as FIA and TIA members. As of the year 2000, the program evaluates the quality and safety of European infrastructures and among the 32 tunnels which have been rated, is the Pont Pla which was one of the 4 only tunnels classified as being "very satisfactory" |
| Arinsal Dam Tunnel |
 Arinsal's dam artificial tunnels were constructed in two phases. The first was the construction of Arinsal's avalanche dam, which was built taking into consideration possible emergencies after the avalanches that occurred in February, 1996. The second phase was completed in 2002.
Arinsal's dam artificial tunnels were constructed in two phases. The first was the construction of Arinsal's avalanche dam, which was built taking into consideration possible emergencies after the avalanches that occurred in February, 1996. The second phase was completed in 2002.
Tunnel 1 has a total length of 183 meters, tunnel 2 of 36 meters (by the river) and tunnel 3 of 95 meters. The artificial tunnels have a "flute beak" shape and a border thickness of 30 centimeters. The part of the artificial tunnel is made of two-round tri-articulated armed plates and has a 16-meter perimeter. The height of the top wall, measured at the center of the tunnel, is of 6 meters. The breadth from side to side is of 8.6 meters, and the width of the pavement is 1.3 meters. A number of pipelines, which urbanize the zone above the tunnel, go through it. Both tunnel 1 and 3 are quipped with lighting on the side of the downward lane, as well as emergency lighting installed laterally along the tunnel's sidewalls. This lighting equipment is regulated through 5 lighting levels. All the tunnels are fully painted. |